Timber is wood suitable for construction purposes. The term “wood” refers to the constituent parts of the tree that carry water and nutrients. Timber is a type of wood. This is used after the tree has fallen or been crushed.
Various Quality tests are carried out in order to determine the quality and sustainability of the Timbers. Timber is a natural polymeric material that almost never ages. Furthermore, the wood’s structure ensures efficient strength and load capacity. Wood is classified into two types. They are both natural and artificial. Plywood, fiberboard, impregnated wood, etc. are a few examples of man-made wood.
Properties of good quality Timber
The timber should possess the following qualities.
- It should have a good uniform dark colour.
- Timber should be free from defects such as shakes, flaws, dead knots, etc.
- It should possess regular annual rings.
- The freshly carved surface of the wood should have a sweet smell.
- Moreover, It should have a heavyweight.
- The cellular tissue and fibres should be compact and hard.
- Good timber should be durable and possess elasticity.
- It should be resistant to fungi, insects, etc.
- Also, timbers with compact textures have good resistance to fire.
- It should be inert from mechanical, chemical and physical agencies.
- Good quality wood should hold loads from structures.
Related articles from Vincivilworld
Also Read: Bitumen – 9 lab tests on bitumen on flexible pavement
Also Read: Bricks – 8 Reliable tests to ensure quality.
Test on Timber
In order to find the quality and sustainability of the Timbers, Various Quality tests are performed. In this article, we have listed a few test procedures.
- Moisture content test
- Tensile strength test
- Compressive strength test
- Shear strength test
- Bending test
Moisture content test of Timber
This test determines the moisture content in wood. However, wood contains a small amount of moisture content. A weighing machine and a drying oven are important apparatuses for the water absorption test.
Relevant IS codes:
IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977
Test procedure
- Initially, Take the specimen with a size of 5cm x 5cm x 2.4cm.
- Then using a weighing machine weigh the specimen. Mark it as W1.
- After that oven-dry the timber at a temperature of 103-degree celsius.
- Later, take out the specimen when becomes dry.
- Again weigh and mark the weight of the dry specimen as W2.
- Finally, calculate the percentage of moisture content by
% of moisture content = Weight of moisture in sample/ Dry weight of sample = (W1 – W2)/ W2
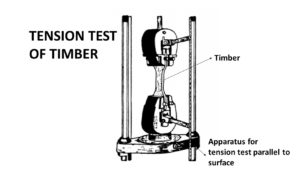
Tensile strength test for timber
The tensile strength test defines the strength and ability to withstand breaking. Also, we can determine the load-carrying capacity of the wood.
Relevant IS codes:
IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977
Test procedure
- Firstly, take a specimen of 5cm x 5cm and 20cm in length.
- Then place the specimen on the base plate of the instrument.
- After that apply load either parallel or perpendicular to the grains.
- Mark the load at which the wood breaks.
- Finally, calculate the tensile strength of the wood.
Tensile strength = Maximum load applied / Cross-sectional area
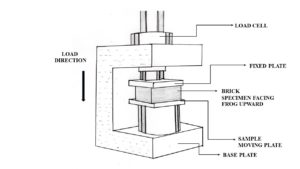
Compressive strength test
The compressive strength test defines the crushing strength of the timber. Furthermore, this test determines the load which the wood can support over a period.
Relevant IS codes:
IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977
Test procedure
- Initially, take a specimen with a size of 5cm x 5cm x 20cm.
- Then place the specimen in the compressive testing machine.
- Following this, apply load parallel to the grains.
- The specimen should be free from defects. Gradually increase the load.
- Then note down the load at which the timber breaks.
- Lastly, calculate the compressive strength from the below formula.
Compressive strength = Load at which the specimen breaks/ Total area of the specimen
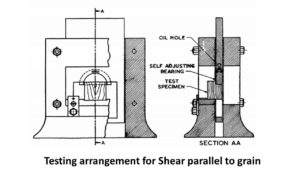
Shear strength test
The shear strength is important when timber is used as slabs. The load should be applied parallel to the grains.
Relevant IS codes:
IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977
Test procedure
- The size of the specimen for shear strength is 5cm x 5cm x6.25 cm.
- Then cut the corner of the specimen.
- Thus it produces failure on 5cm x 5cm surface.
- However, this failure occurs tangentially or radially.
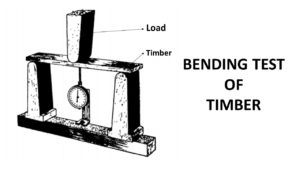
Bending strength test
The Bending strength test is necessary when we use timber as a beam. Through this test, we can find the modulus of rupture and modulus of elasticity.
Relevant IS codes:
IS I 2380 ( Part VI ) – 1977
Test procedure
- For this, take a specimen of 5cm x 5cm x 7.5 cm in size
- The specimen should be free from defects and deterioration.
- Then drop a hammer with a specific weight from a certain height.
- Thus we get the impact bending.
- Lastly using the load and deflection, calculate bending strength.




3 comments
Comments are closed.