Micropiles
Micropiles are introduced as an efficient and cost-effective alternative to conventional pile foundations. Micropiles possess the capability to withstand heavy loads and can be installed with compact and sophisticated machinery using cutting edge technology. The main advantage of a micropile is its ability to work in very congested and low height areas and on any soil surface irrespective of its type. Micropiles are best suited for piling, retrofitting & underpinning works, slope protection, soil stabilisation, etc. Another important feature of micropile is their ability to work with minimum disturbance to the existing structures and people around the area. Micro piles provide a very reliable and cost-effective alternate which is becoming an inevitable part of urbanisation.
ALSO READ : PILE FOUNDATIONS– Types Advantages and Method of Installation
What are Micropiles?
Micropile is a bored /drilled cast in place friction piles having diameter ranging between 50 mm to 300 mm. The drilled / bored holes are grouted with cement after placing the reinforcement bars. They can withstand axial loads, lateral loads, or both and can negotiate loads ranging between 3T to 300T and more. Micropiles are known as mini piles, pin piles, root piles, etc based on their applications. The micropiles can penetrate any obstructions that can sometimes cause premature refusal while installing using conventional piling methods.
Components of Micropiles

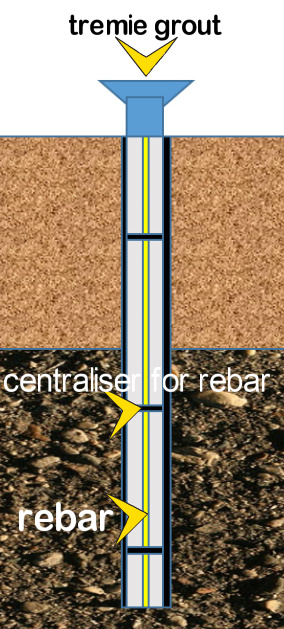
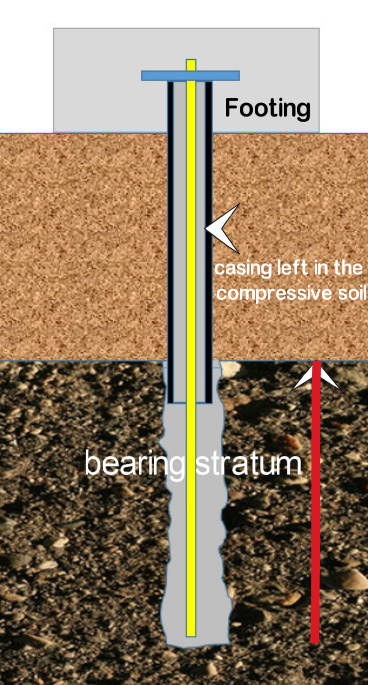
The figure represents a typical section of a micropile resting on a hard soil/ rock strata. The steel casing is restricted to the compressive strata. The casing extends a bit into the hard strata for some anchorage. The surface area of contact between the ground and the concrete below the casing is known as bearing stratum.
Reinforcement used in Micropile
The reinforcement used in micropiles are divided into four categories
| a) Standard rebar cage with centraliser |
| b) API pipe system |
| c) Solid threaded rebars with or with out pipe casing |
| d) Hollow bar or Drill hollow bar system |
Standard Rebar Cage
The rebar cage is the same as the cage used in conventional piling. Threaded couplers are used to join the bars together with staggered joints. A centraliser (as per fig) is used for positioning the rebar cage inside the bore.
API Pipe System

API pipes (American petroleum Institute pipes ) are high-grade pipes having a diameter of 5 inches to 11 inches. These pipes are joined using high strength machined flush type joint threads. Both inside and outside of the API pipes shall be grouted with or without placing rebar. Centrally reinforcing type of solid threaded or standard rebar type (ref fig) can be used as rebar. API PIPE SYSTEMS are recommended for compression piles to maintain their lateral stability.
THREADED SOLID REBAR SYSTEM
Threaded solid rebar can be used alongside permanent/temporary casings and with API pipe as central reinforcements. Solid threaded rebar constitutes a full threaded high strength bar which can be cut and jointed as per requirements. These bars not only functions to produce full tension and compression capacity but also enhances much-needed bonding with the grout.
Hollow Threaded Bar or Drill Hollow Bar System

The hollow threaded rebar system is also known as a self-drilling hollow bar system. In this system, the hollow bar can function as a sacrificial drill bit which gets converted to a central reinforcement and can also be used to flush out the debris. This system can eliminate predrilling, frequent removal of pipes and drills, etc and can handle any condition relating to the installation of micropiles. On completing the final stage of drilling, the cement mortar is injected into the hollow core of the drill bit by an injection adaptor (ref fig) mounted with the drilling unit. The grout flushing simultaneously serves in stabilising the borehole and filling the area.
Drilling Methods for Micropiles
The installation process of micro piles involves drilling or driving a bore through soils, rocks, overburden, etc. The most common methods adopted for drilling are:
Percussive Drilling used with a driving point/drill at the bottom of the permanent casing is defined as displacement method . When air is used as a flushing medium then the method is called non-displacement method.
Rotary drilling uses air or water as a flushing medium for removing the drilled materials from the drill hole. The air jet or water pumped through the drilling system exit at the drill bit end flushing out the cuttings.
Grouting Methods of Micropiles
Grouts used for micropiles constitute a mixture of cement and water. Sand can be added as per design requirements to reduce the overall cost. The micro piles are divided into four types based on the method of grouting
TYPE A – Micropiles
Type A micropiles use tremie grouting and through gravity head. The grouting is started from the bottom and follows a similar tremie grouting procedure followed in conventional piles.
TYPE B – Micropiles

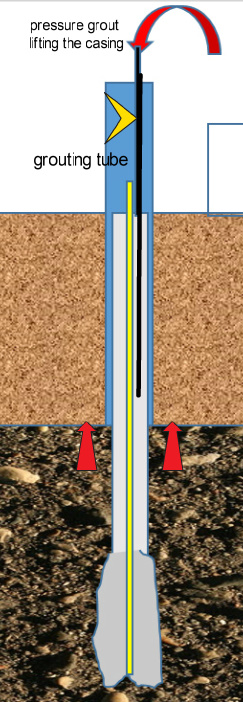
After performing the initial tremie grouting, a pressure grouting is followed simultaneously with the lifting of the casing from the bond zone. The second stage pressure grouting is done through a preinstalled tube. Second stage grouting serves in enhancing grout soil bonding. The grouting will be done up to the bearing stratum and can be extended to the full length of the pile if required.
TYPE C – Micropiles
In these types of piles, pressure grouting is followed by tremie grouting. On completion of pressure grouting, a global injection grouting is performed through a pre-installed sleeve port pipe. This grouting shall be done before the hardening of primary tremie grout.
TYPE D – Micropiles
This method is similar to Type C . In this method primary grout is done under pressure and after hardening secondary grout is done through installed sleeve ports. Packers are also provided for multiple injections.
Methodology of Installation of Micropiles

a) Drilling is done using a rotary rig or Rotary percussive drilling machine with casing attached to the drill bit. The casing is simultaneously pushed with the drill bit.
b) On reaching the founding level the drill bit is removed with casing left in the borehole.
c) Place reinforcement with centraliser in the borehole and followed by tremie grout with cement water mix.
d) The tremie grouting will be followed by a pressure grouting through preinstalled grouting tubes with simultaneously lifting of the casing.
e)The casing lifting to be done up to the compressive soil level with adequate bearing to the hard strata. (ref.fig) Complete pressure grouting of the bearing stratum area.
WHY MICRO PILE IS PREFERRED AGAINST CONVENTIONAL PILE?
a) Micropiles can be engaged in any challenging conditions involving soil and rock..
b) Micropiles can be customised and applied for difficult terrains and applications. The applications can either be in the form of new loads being added to an existing structure, for arresting structural settlement, for resisting uplift and dynamic loads, for seismic retrofits or works involving underpinning and slope stabilisation.
b) Micropiles are used for rehabilitation projects as well as new constructions in difficult and access constraint terrains and settlement prone locations. For rehabilitation works in congested and low headroom height basements, micropiles prove to be a preferred option.
c) Micropiles penetrate any surface and can be installed even through an existing foundation making it one of the best possible solutions for foundation rehabilitation and strengthening works.
d) Micro piles can be used for slope stabilisation, embankment stabilisation, and other soil improvement and ground improvement works.
e)Micro piles can be used in areas where water table is high, urban back fills, areas having floating boulders or other difficult terrains that can’t even be accessed with a conventional pile.
d) Used extensively in the rehabilitation of monuments, old structures, sinking structures etc in all parts of the world.
Conculsion.
Micropiles are emerging as a perfect cost-effective option without any alternatives. Because of its design flexibility and wide range of applications micropiles are gradually entering into urban destiny.