Types of foundations – This article focuses on different types of foundations used in civil engineering. The foundation is the most crucial component of any structure/building because it transfers the total loads of the structure and its components to a competent ground surface. There are two types of foundations. ie: Shallow foundations and deep foundations
Types of foundations – How to decide?
The foundation is the most essential element of a structure. A well-designed foundation is critical to protecting a structure from dead loads, live loads, and external forces acting on the structure. The foundation is the final part of the structure to make contact with the ground. The foundation bed is the area where the foundation meets the ground. Before we get into the different types of foundations, let’s converse about substructure and superstructure. Each structure is subdivided into Superstructure & Substructure Substructure refers to components of a structure that are below ground level, while superstructure refers to components that are above ground level. The foundation belongs to the substructure category and is responsible for transferring loads from superstructure components to the ground.
Deciding the size and types of foundations
The type of foundation is determined by the soil’s bearing capacity and the purpose of the structure. Geotechnical engineering is a branch of civil engineering that analyses the physical and chemical properties of soil in order to provide input to designers on soil properties and proposed foundation types and sizes.
Safe bearing capacity
A soil’s bearing capacity is its ability to support a structure without settlement or failure. The bearing capacity of soil must be calculated at various locations to ensure the structure’s safety. To determine the safe bearing capacity of the soil, the ultimate bearing capacity should be divided by a factor. The maximum load per unit area that soil can withstand without settlement and failure is defined as safe bearing capacity. Field tests or soil investigations are often used to determine the safe bearing capacity of the soil.
Types of foundations
Foundations are broadly classified into
For more details about shallow and deep foundations please follow this article
Types of foundations – Shallow and Deep Foundation
Types of shallow foundations – Advantages & Suitability
Deep Foundation types – A Detailed overview
Shallow foundations
Shallow foundations transfer the load to the soil laterally. It’s also known as stripped foundations. A shallow foundation has a depth that is less than its width. Shallow foundations are used when the load acting on a structure is reasonable and there is a competent soil layer capable of negotiating the loads available at a shallow or shorter depth. A shallow foundation is laid on the ground’s surface. A shallow foundation’s depth can range from 1 meter to 3.5 meters, and sometimes even more.
Types of foundations – Shallow foundations
Shallow foundations can be of various types, depending on the site conditions and design requirements.
Spread footing or isolated footing
The spread footing is one of the most common types of shallow foundations. They are also known as isolated footings or individual footings. Spread footings are further classified based on their shape into simple spread footing, sloped spread footing, and stepped spread footing.
- Simple spread footing
- Sloped spread footing
- Stepped spread footing
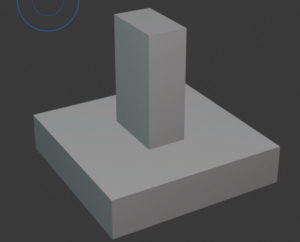
Simple spread footing
A simple spread footing is made up of a base footing and a single column on top of it. This foundation is used for structures with reasonable/moderate loads and bearing capacities.
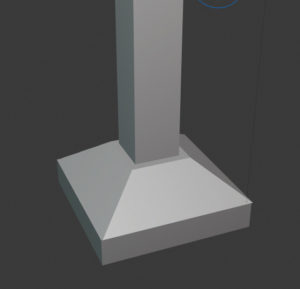
Sloped spread footing
Footings in this type of foundation are sloped, as shown in the figure. The footing is supported by a single column and has a trapezoidal cross-section.
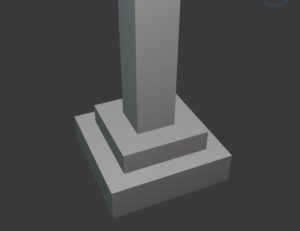
Stepped spread footing
When the loads are heavy, steps are provided in the footings, as shown in the figure.
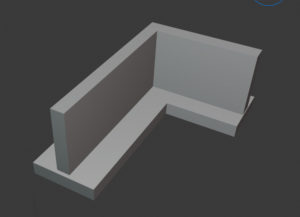
Strip footing
Strip footings are also known as wall footings. They are used to provide load-bearing brick/stone/RCC walls over the footings. Strip footings run continuously along a building’s wall. These footings are also used when the column spacing is very close and the footings overlap.
Combined footing
A combined footing is made up of two or more columns laid over a single footing. These footings are used when the distance between two individual footings is very small and they overlap. A combined footing is also provided in areas where further excavation is not possible due to boundary flushing. Rectangular combined footings and trapezoidal combined footings are the two types of combined footings.
- Rectangular combined footings
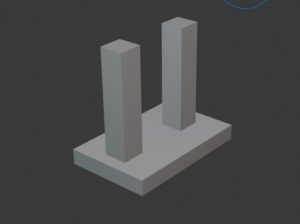
- Trapezoidal combined footings
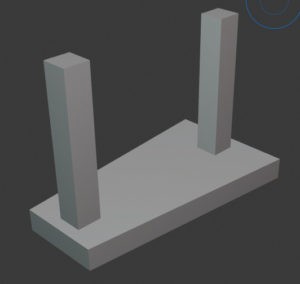
Strap footing
Strap footings, also known as cantilever footings, are made up of two individual footings connected by a beam strap. The beam strap is designed as a rigid structure. These types of foundations are less expensive than combined footings.
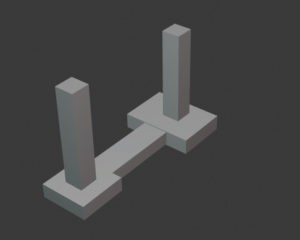
Types of foundations – Raft foundation /Mat foundation
Raft foundations are the most common foundation types used in construction. It is a continuous slab that rests on the soil and covers the entire area of the proposed structure. Raft foundations are categorized based on their intended use. Numerous factors, such as bearing capacity, loads, site conditions, and so on, influence the type of raft foundation. A raft foundation/mat foundation is a solid slab which spans the entire structure area and is placed at a predetermined depth. Raft foundations are comprised entirely of columns and shear walls which transfer the structure’s load to the ground. These foundations are generally used when the soil’s bearing capacity is low and individual footings struggle to negotiate the loads. The raft foundation aids in the transfer of the entire load of the structure to a larger area.
For more information on raft foundations, please see our blog: Raft foundations – Types and Advantages.
Types of foundations – Deep foundations
The foundations having a depth more than the width are called deep foundations. When the subsoil strata lack the safe bearing capacity to handle the loads induced by the structure, deep foundations are proposed. In such a case, the foundations’ founding level is moved to a deeper area with the required bearing capacity. The structure’s loads are transferred vertically into the ground.
Many applications adopt deep foundations. They are considered the safest option for transferring heavy loads on soil strata with low bearing capacities. The following are examples of common Deep foundations in use.
- Basement foundations
- Caissons Foundation
- Hollow Box Foundation or Buoyancy foundations
- Drilled shaft foundations
- Pile foundations
Pile foundations
Pile foundations are long, slender members made of concrete, steel, or any other material which are used to transfer loads from a structure when the subsoil lacks bearing capacity. The pile foundations transfer the load vertically through the less dense top layer to a denser soil/rock layer which can negotiate the loads without failure.
For more details read our article: Pile foundations – Types and advantages
Basement foundations
Basement foundations are substructure foundations designed to account for parking areas, underground tanks, electrical systems, and storage spaces beneath a building below ground level. They are commonly used in high-rise residential and commercial structures. Basement foundations are designed to address the functional needs of parking and storage.
Caissons foundation
A caisson foundation is a water-retaining structure that serves as a working space for pier foundation operations. They are box-like constructions built of wood, steel, concrete, and other materials. Caisson Foundation is sunk by excavating the earth within the foundation. Caissons are prefabricated above ground or water level and sunk to the founding level as a single unit. They are built to facilitate excavation and related operations for dock structure foundations, bridges, jetties, piers, foreshore protection, and so on. These structures are eventually incorporated into the main structural components.
Hollow box foundations or Buoyancy foundations
The concept behind a hollow box foundation is to create a structure that has little or no impact on the original soil stress before commencing excavation. Overburden is removed as required by the design, and superstructure loads are transferred to the ground. These foundations are referred to as buoyancy foundations because they follow the principle of a ship floating in the water, where the displaced water balances the ship’s weight.
Drilled shaft foundation
The drilled shaft is a versatile foundation system that is widely used nowadays. These foundations are also referred to as drilled piers, drilled caissons, bored piles, and so on. The main idea is to excavate a cylindrical shaft and then cast it after adding the necessary reinforcements. Drilled holes should be between 1-3 meters in diameter and up to 100 meters deep. Shafts can be drilled to depths of 100 meters and diameters varying from 1 to 3 meters. However, greater depth and diameter are now conceivable. These foundations can partially replace driven piles in the same way that a single drilled shaft can replace a group of piles.
Conclusion
Shallow foundations are very easy to construct and do not require highly skilled manpower and professional supervision. These foundations can even be built with the assistance of semi-skilled workers. A shallow foundation is very economical when compared with a deep foundation. Shallow foundations are end-bearing type foundations that transfer loads to the end of the foundation. Shallow foundations are considered the most preferred option when the safe bearing capacity of the soil is reasonable and the structural loads are within the permissible limits.


4 comments
Comments are closed.